quantitative spectrophotometry|Spectrophotometer: Principle, Instrumen : wholesale Spectrophotometry is a technique used to measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted. reflected, and/or emitted by a substance as a function of its wavelength, concentration of the sample, and path length or distance the light traverses through the substance.¹ It is widely employed in chemistry and biology for quantitative analysis of substances, such as .
WEBSeason 2. BMF returns for a second hit season and dramatizes the inspiring true story of two brothers who gave birth to the influential crime family, Black Mafia Family. Determined to achieve their American .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Busca por - Fatal Model. Dúvidas Frequentes. Voltar ao site. Página inicial.
These methods can provide, for example, qualitative information concerning molecular formulas and bonding, and quantitative information regarding the energy levels and the concentrations of the absorbing species. Here are your results for the lab! The k-values correlate with the slopes of each line of best fit. For example, the k-value of Cr 3+ at 510 nm is equal to the slope of that graph’s . Spectrophotometer is widely used in the quantitative pharmaceutical analysis. In quantitative pharmaceutical analysis, the unknown concentration of analyte may be determined with the help of absorption spectrophotometry because most of the biological organic compounds have the ability to absorb EMR in UV-VIS region.
For convenience we will use the simpler term spectroscopy in place of optical spectroscopy; however, . Normally a fixed-wavelength monochromator is used for a quantitative analysis where measurements are .
Spectrophotometry
Spectroscopy in Forensic Science☆ M.B. Eyring, P. Martin, in Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering, 2013 Spectrophotometry (SP) Spectrophotometry can be an extension of any of the foregoing types of spectroscopy. It is a term that refers to the quantitative analysis of spectra to compare the relative absorption or .Spectrophotometry is a technique used to measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted. reflected, and/or emitted by a substance as a function of its wavelength, concentration of the sample, and path length or distance the light traverses through the substance.¹ It is widely employed in chemistry and biology for quantitative analysis of substances, such as . UV-Vis Spectroscopy or Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (UV-Vis) is also called absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. . It is a qualitative, quantitative, and analytical technique that compares a sample with a blank or reference sample to .Papers with the following subject areas are suitable for publication in the Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer: Spectra of atoms, molecules: theoretical and experimental aspects; Spectral lineshape studies including models and computational algorithms; Spectroscopy of the . View full aims & scope $
Generally, protein quantitation can be made using a simple UV-Visible spectrophotometer. The V-630 Bio (Figure 1) is a UV-Visible spectrophotometer designed for biochemical analysis. The V-630 Bio includes 6 quantitative methods based on UV absorption spectrophotometry including the Lowry, Biuret, BCA, Bradford, and WST methods.DNA concentration can be determined by measuring the absorbance at 260 nm (A 260) in a spectrophotometer using a quartz cuvette.For greatest accuracy, readings should be between 0.1 and 1.0. An absorbance of 1 unit at 260 nm corresponds to 50 µg genomic DNA per ml (A 260 =1 for 50 µg/ml; based on a standard 1 cm path length. This relation is valid only for .
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy is a widely used technique in many areas of science ranging from bacterial culturing, drug identification and nucleic acid purity checks and quantitation, to quality control in the beverage industry and chemical research. This article will describe how UV-Vis spectroscopy works, how to analyze the output data, the technique's .spectroscopy and atomic emission spectroscopy are also being used for quantitative measurement of different substances or elements. Keywords: spectroscopy, spectrophotometry, UV-visible spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray fluorescence 1. Introduction Every compound, that is present in the nature, has a .
Infrared spectra of 13 globular proteins have been obtained in the 1800-1480-cm-1 region for H2O solutions. A method for estimating protein secondary structure from the ir spectrum has been developed. The method can also be used for estimating polypeptide and fibrous protein conformation. For the gl . Moreover, the amount of absorbed light is related to the amount of sample, and thus, quantitative analysis is possible by optical spectroscopy. This article more specifically explores techniques when using a spectrophotometer to determine .
In the present study, the spectrophotometry method for quantitative analysis of starch/iodine complex in low-concentration starch samples, such as bioaerosols, was tested and optimized. The MDL for starch in low-concentration samples using the Perkin Elmer Lambda 1050 UV/Vis spectrophotometer is 0.22 μg/mL, and the LOQ is 0.79 μg/mL. The quantitative analysis using UV–visible spectrophotometry is based mainly on the Beer-Lambert law, which explains the relationship between the absorbance of analyte under analysis and its concentration: . British Pharmacopeia, USP, EP, etc. Hence, spectrophotometry is generally preferred in small-scale industries and most laboratories .Quantitative IR spectrophotometry of peptide compounds in water (H2O) solutions. I. Spectral parameters of amino acid residue absorption bands Biopolymers. 1990;30(13-14):1243-57. doi: 10.1002/bip.360301309. Authors Venyaminov SYu 1 , .
The spectrophotometer is essential in quantitative analysis of biochemistry practical such as in determining the unknown concentration of a given species through absorption spectrometry. A perfect example is the .
Objective: This study aims to establish a spectrophotometry method to determine the content of total flavones from Polygonatum sibiricum. Methods: Rutin was used as the control substance. After the color reaction of Al (NO 3) 3-NaNO 2-NaOH system, the maximum absorption wavelength was determined and the standard curve was drawn. Then the .An example of a UV/Vis readout. UV/Vis can be used to monitor structural changes in DNA. [8]UV/Vis spectroscopy is routinely used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of diverse analytes or sample, such as transition metal ions, highly conjugated organic compounds, and biological macromolecules.Spectroscopic analysis is commonly .Spectrophotometry is the quantitative measurement of how much a chemical substance absorbs light by passing a beam of light through the sample using a spectrophotometer. In this video, basic concepts in spectrophotometry, including transmittance, absorbance and the Beer-Lambert Law are reviewed in addition to the components of the .
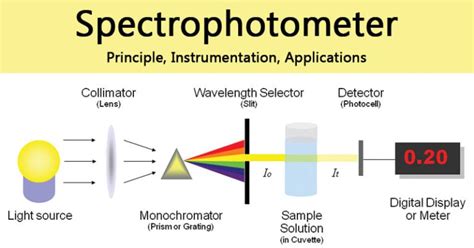
Spectrophotometry is the quantitative measurement of the interaction of ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) radiation with a material and has an impact on a wide field of science and technology. The nature of this interaction depends upon the physical properties of the material, for example, transparent or opaque, smooth or rough, pure .Spectrophotometer Instrumentation. A spectrophotometer is made up of two instruments: a spectrometer and a photometer. The spectrometer is to produce light of any wavelength, while the photometer is to measure the intensity of light. The spectrophotometer is designed in a way that the liquid or a sample is placed between spectrometer and .Values for ε and l. Path length l is usually in units of cm. (note: most spectrophotometers are designed to accept 1cm wide cuvettes) Molar extinction coefficient ε has units of M-1 cm-1 and is a constant of proportionality that relates the absorption of molar solutions; Mass extinction coefficient ε 1% refers to the absorbance of a 1% by mass solution. . Typically this refers to an .This chapter focuses on quantitative molecular absorption spectroscopy, one of the most important and common applications of spectroscopy. The word quantitative means measuring the concentrations of the chemical species in a sample. The word molecular relates to the molecules, not the atoms or elements in a sample.
Keywords: infrared, Raman, first and second derivatives, qualitative and quantitative estimations, hyphenated techniques 1. Introduction The introduction included the followings below: 1.1 Infrared spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the branch of science contracts with learning about the interaction of the radiation of electromagnetic rays with .
Infrared spectroscopy is a technique that has acceptable accuracy and sensitivity to be one of the most important analytical techniques used in the qualitative analysis, and also, it is used in the quantitative estimation of compounds through measuring the transmitted or absorption intensity of the active groups.
Applied spectrophotometry: analysis of a biochemical mixture Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2013 Jul-Aug;41(4):242-50. doi: 10.1002/bmb.20694. Epub 2013 Apr 27. Authors Toni A Trumbo 1 . demonstrate the utility and limitations of example quantitative colorimetric assays, demonstrate the utility and limitations of UV analyses for biomolecules, develop . Spectrophotometry allows both qualitative and quantitative analysis. As the concentration of a substance increases light absorption increases, and light transmission decreases. Spectrophotometry is used in chemistry, biochemistry (for enzyme-catalysed reactions), physics, biology, and clinical studies (examining haematology or tissues).
speck candyshell galaxy s4 drop test
speck candyshell grip case drop test
Spectrophotometer: Principle, Instrumen
7: Quantitative Spectrophotometry and Beer's Law (Graph)
webPS5. PlayStation®5. PlayStation®5 Digital Edition. Experience lightning-fast loading with an ultra-high-speed SSD, deeper immersion with support for haptic. feedback, adaptive triggers, 3D Audio, and an all-new generation of incredible PlayStation® games. Harness the power of a custom CPU, GPU, and SSD with Integrated I/O that rewrite the.
quantitative spectrophotometry|Spectrophotometer: Principle, Instrumen